Rehabilitation after a fracture of the radius of the hand
WHO defines rehabilitation as follows: "It [rehabilitation] includes all means to mitigate the severity of restrictive and adverse conditions, allows a person to achieve social integration." It follows from the definition that rehabilitation is aimed at solving a wide range of problems, not only medical, but also social, educational, and professional. All rehabilitation procedures, incl. development of the hand after a fracture of the radius, should be based on the needs of the patient.
The content of the article
What to do after plaster removal
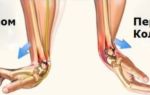
A fracture of the radius is one of the most common fractures in the human body, mainly caused by a fall.
The basis of treatment is closed reduction (moving the broken bone to its original position) and subsequent plaster fixation. Already during immobilization, it is important for the injured person to train the fingers and the shoulder joint. The development of the fingers should be carried out several times a day. It is necessary not only to move them, but also to train them in all directions, to bring the movements to the level allowed by the plaster splint. Slight swelling of the fingers is not a reason for not exercising.
After removing the cast, the movements of the arm and wrist become tense and painful. Properly selected rehabilitation will help restore mobility. It is important to start with simple movements, gradually increase the complexity of each exercise. Initially, training will be painful, which is important to keep in mind. The pain subsides a few minutes after the start of the exercise.
Hand care after plaster removal:
- Bathe your hand in warm water (20-25°C); it is better to apply a lower temperature than a high one. Using a sponge, gently rub it in the water. Do not scratch the skin, do not try to completely clean it on the first wash. It is good to squeeze the sponge in water several times with the fingers of the affected hand. Do not squeeze the sponge for more than 5-10 minutes. Bathe spend 1-2 times during the day.
- Dry the washed hand, apply a greasy cream. Lightly massage it, rubbing the cream. In the area of \u200b\u200bthe fingers, you can press, massage your fingers from all sides.
- After washing, start your workout. The first and simplest exercise to help develop a hand after a fracture of the radius, to return the limbs to their original function, is the following. Spread a thick terry towel on the table. When performing exercises, the hand should be on the table with a relaxed shoulder and elbow. Move your palm and forearm across the towel. The exercise is aimed at restoring the mobility and functional abilities of the hand.
- To eliminate the increase in pain after exercise, it is recommended to use a cold compress on the wrist and fingers. Place ice cubes in a microtone bag, wrap your hand in a cotton towel, and apply an ice bag. For compresses, you can also use cold water, for example, cold wine wraps (wine is mixed with water in equal proportions).
- It is useful to support the treatment with some nutritional supplements, drugs.
- In the first days after the removal of the cast, the hand is on the latch; during sleep, it should be placed under a pillow to minimize swelling of the fingers.
- A few days after the release of the fixator, the area of the radius is bandaged with an elastic bandage, and later, for safety, it can be bandaged with a hydrophilic bandage (ordinary gauze). This ultra-light fit is mainly used when outdoors, on the road, etc.
- Gradually, the affected hand is included in daily activities, which is also a form of training (combing hair, washing, writing, opening doorknobs, holding a spoon, doing handicrafts, etc.).
If the hand is excessively warm, red, visibly swollen and painful, the skin is shiny and tight, a visit to a doctor is required. This may be one of the complications requiring treatment.
Rehabilitation exercises
Physical exercise is the main method of how to develop a hand after a fracture of the radius. Their goals:
- pain reduction;
- optimization of musculoskeletal function;
- improving the quality of life;
- strengthening and thickening of the bone.
Practical tips for rehabilitation exercises
In the first days after surgery, the goal of extremity care is to prevent swelling or speed up its elimination. Swelling under the cast can overwhelm the patient's nerve vascular and muscle structures, which, if not properly managed and rehabilitated, can lead to long-term damage to the entire hand. Therefore, in the first days after the fracture, it is necessary to monitor the swelling of the fingers and around the cast, and in case of pain and twitching, consult a doctor.
The gypsum should always fix only the affected area, the rest of the joints should remain free. After the pain at the fracture site has been relieved, it is helpful to start exercising the fingers to prevent stiffness. During training under the influence of the so-called. the muscle pump eliminates edema, improves blood flow, and consequently, resorption of the bruise. Hematoma, bluish in the first days, and then green, yellow and disappearing, first appears in the elbow area. If it appears on the fingers, it indicates poor positioning of the limb.
You can develop a hand after a fracture of the radius using the following workouts.
Exercise #1
The goal is to support the muscle strength of the fingers. A foam ball or sponge is used.
Take a ball or sponge in the palm of your hand, squeeze it slowly. Squeeze until you feel tension, not pain. Exercises are performed in 2 series 2-3 times a day. If after training there is no pain at the fracture site, the following exercises are gradually added.
Exercise #2
Relaxation of the wrist and fingers. With both hands, lean on the elbow joints on the table, gradually tapping the fingers of one hand on the wrist of the other.
Train until you feel slight pain before and after each subsequent exercise.
Exercise #3
Wrist to palm curl training.
Rest the injured upper limb with your elbow on the table, and with the other hand, grasp the lower part of the forearm. Try to bend your wrist. In the extreme position, if you feel tension, but not pain, leave your arm in a bent position for 10 seconds, then gradually relax. In the early days, train your wrist for 2 series 2-3 times a day.
Exercise #4
Another variation of the wrist flexion workout.
Rest your injured upper limb on a table with your elbow. With the thumb of the other hand, support the forearm, with the free part help to bend the wrist. Again, leave your arm in a bent position for 10 seconds, then gradually relax. Do 2 sets 2-3 times a day.
Exercise #5
Thumb forearm rotation training. Rest your injured arm with your elbow on the table with your thumb facing you. Grasp your wrist with your other hand, placing your thumb on the back of your wrist. Gradually roll your forearm behind your thumb. With the other hand that holds the wrist, help scroll until you feel a slight (!) Pain. In the extreme position, linger for 10 seconds, then gradually relax your hand. Do 2 sets 2-3 times a day.
If finger movement or muscle strength is limited, wrist mobility exercises are done very slowly and carefully. Remember that the hand is a single complex part of the body. With a fracture of one area, all other areas of the limb are violated.
Rehabilitation after a fracture of the radius of the arm also includes a number of other methods. All of them should be performed either in a complex, or in accordance with the patient's condition.
Therapeutic rehabilitation
Medical rehabilitation is an integral part of caring for a patient with a fracture of the radius. It includes a set of rehabilitation, diagnostic, therapeutic and organizational measures aimed at maximizing the improvement of a person's physical form, creating conditions for the successful restoration of a limb.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy is a treatment that uses several different forms of energy, including movement to relieve painful conditions. Physiotherapy is used to influence the motor system. Its purpose is to analyze the musculoskeletal system and influence not only it, but also other organs and systems.
Kinesiotherapy
It is an important and indispensable component of therapeutic rehabilitation. It uses the knowledge of anatomy and neurophysiology of the human body, improves the function of both the motor system and internal organs. Due to the complex action, kinesiotherapy can also affect the psyche. With a permanent dysfunction, this rehabilitation method finds a compensatory replacement; in degenerative and progressive diseases, it maintains the function for the longest possible time.
physical therapy
Physical energy therapy, using both natural and technical energy, uses the knowledge of the impact of physical effects on pain reduction, healing of affected tissues.
Therapy using natural physical energy is called balneology.
Ergotherapy
It is a rehabilitation method that works through meaningful employment. It seeks to preserve and use the human ability to cope with everyday professional, leisure and recreational activities. Suitable for people of all ages with different types of fractures. The concept of employment includes all types of activities performed by a person during his life, perceived as part of his lifestyle, individuality.
Physiotherapy during immobilization
The choice of method for restoring a hand after a fracture of the radius should be considered already at the time of immobilization. Casting is not an obstacle to training the surrounding joints and segments of the injured upper limb. It is even necessary; exercises during immobilization are very important for a quick recovery. Patients who do not train their joints may subsequently have problems with the movement of the hands, elbows, shoulders. This will lead to a significant prolongation of rehabilitation and other complications.
Important is the positioning of the limb, preventing swelling, training isometric muscle contraction, providing muscle movement in a fixed joint.
Active exercises for fingers and other joints
Active training of the segments surrounding the affected radius maintains their good functional condition, as well as overall performance, which can quickly decline during immobilization. It is important to start exercising as soon as possible in order to reduce the overall catabolic metabolism setting in case of a sudden decrease in physical activity.
All functional finger movements are trained. But also we must not forget about the joints of the upper limb, located proximal to the wrist. The elbow is practiced by flexion-extension, the shoulder in all movements. During exercise, the patient can be in a supine, sitting or standing position.
Positioning of the upper limb
Elevating an extremity with a fractured radius reduces the chance of edema and venous complications. This prophylaxis mainly serves to drain intravasal and extravasal fluids. In addition to reducing edema, positioning prevents blood stasis in the venous system, which can lead to thrombotic and inflammatory venous complications.
All patients with a fracture of the radius should be positioned so that the wrist is above the level of the elbow and the elbow is above the level of the heart. This position does not depend on the position of the body itself (lying, sitting, standing).
But incorrect positioning sometimes causes pinching syndrome. Another risk is prolonged elbow flexion, which can irritate the ulnar nerve.
Rhythmic initiation of movements
This is a rhythmic technique that uses the full range of motion, but without stretching the muscles. The movements are initially passive, carried out by the therapist. The patient then assists the therapist and finally moves independently. After successful initiation, the therapist can create resistance to the patient. The purpose of this technique is to develop a hand after a fracture of the radius by improving movement initiation, movement control, and relieving increased muscle tension.
contraction-relaxation
The contraction-relaxation technique is mainly designed to reduce muscle tone and increase range of motion. The basic principle of this method is the contraction of shortened muscles with a dynamic component through rotations followed by relaxation (passive movement conducted by the therapist).
Combined techniques
As part of the rehabilitation after a fracture of the radius, you can use a combined technique based on the effects of agonists and antagonists, containing 3 techniques.
- rhythmic stabilization. A technique that uses purely isometric contraction. The patient holds a certain position while the therapist tries to deflect him.
- Dynamic handling. A method in which there is a constant resistance to the contraction of agonists and then antagonists without the possibility of relaxation. Movement is smooth.
- Stabilization. The therapist changes the resistance or pressure, if necessary, the direction of the resistance. As resistance increases, muscle strength develops and resistance is used for stabilization.
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF)
Today PNF is a neurophysiological concept with a wide range of indications. Its essence lies in the targeted control of motor neurons through the anterior corners of the spinal cord. It is mediated by afferent impulses from proprioreceptors in the muscles, tendons, and joints, and efferent impulses from the brain that respond to afferent impulses from tactile, visual, and auditory exteroreceptors.
The main role of the PNF is to perform the movement of the affected limb with the affected radius bone by the therapist, using passive, partial auxiliary or active movements of the patient. A very important factor is the correct holding of the patient. For this, a lumbar grip is used, which allows targeted resistance. Another positive point is a significant tactile stimulus.
In conclusion: what not to do after removing the cast
After removing the cast, the hand at first glance seems ugly. The skin is scaly, ugly, often unpleasantly smelling. You should not try to immediately eliminate these shortcomings, return the limbs to their original appearance by soaking in hot water. This procedure will lead to significant swelling.
Another mistake is the free lowering of the arm along the body immediately after removing the cast. In this case, there is a risk of severe swelling of the fingers. In the affected hand, you can not carry heavy objects, overstrain it.